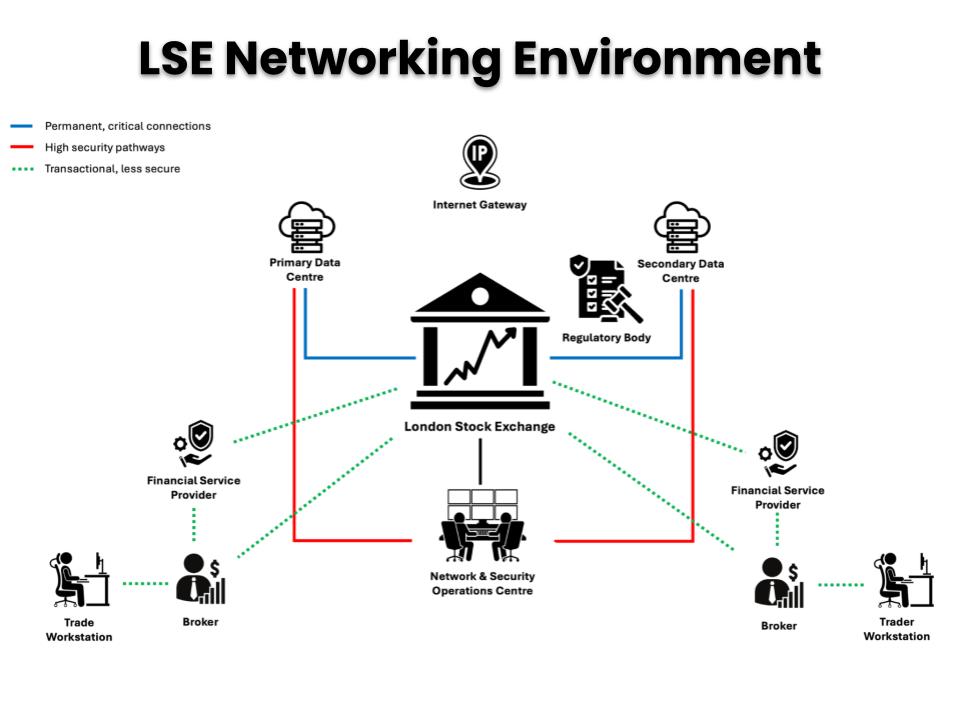
Network Environment
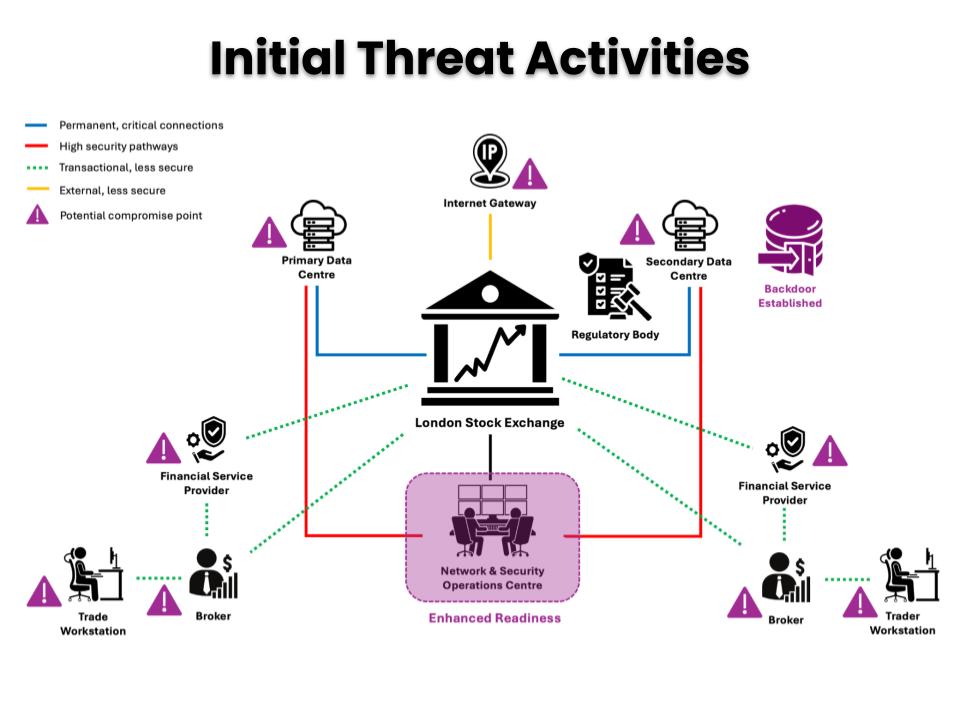
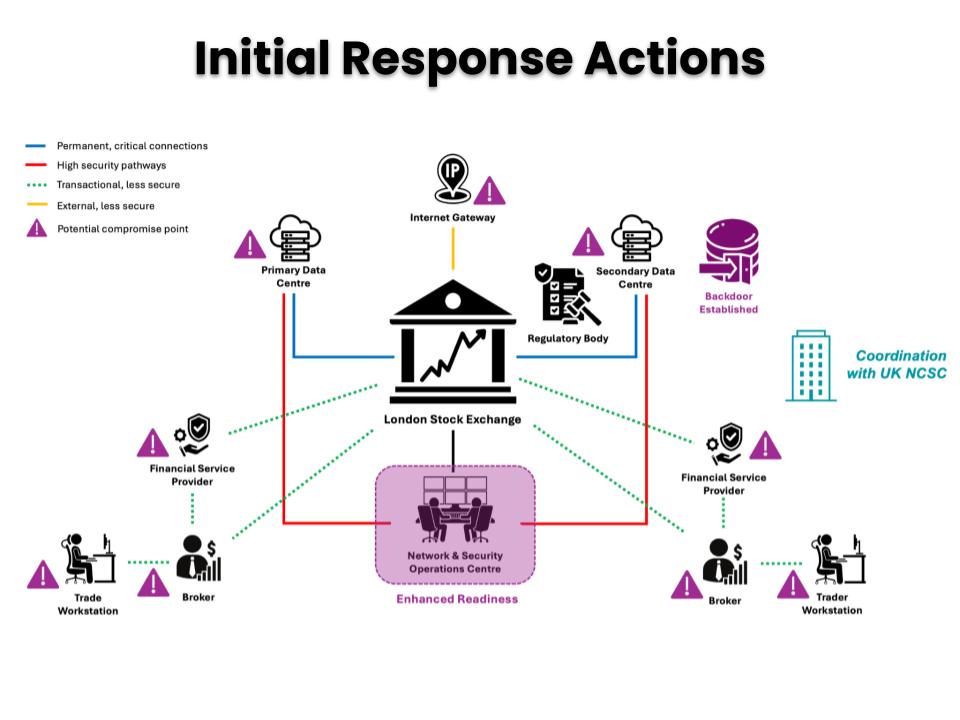
Mission Parameters
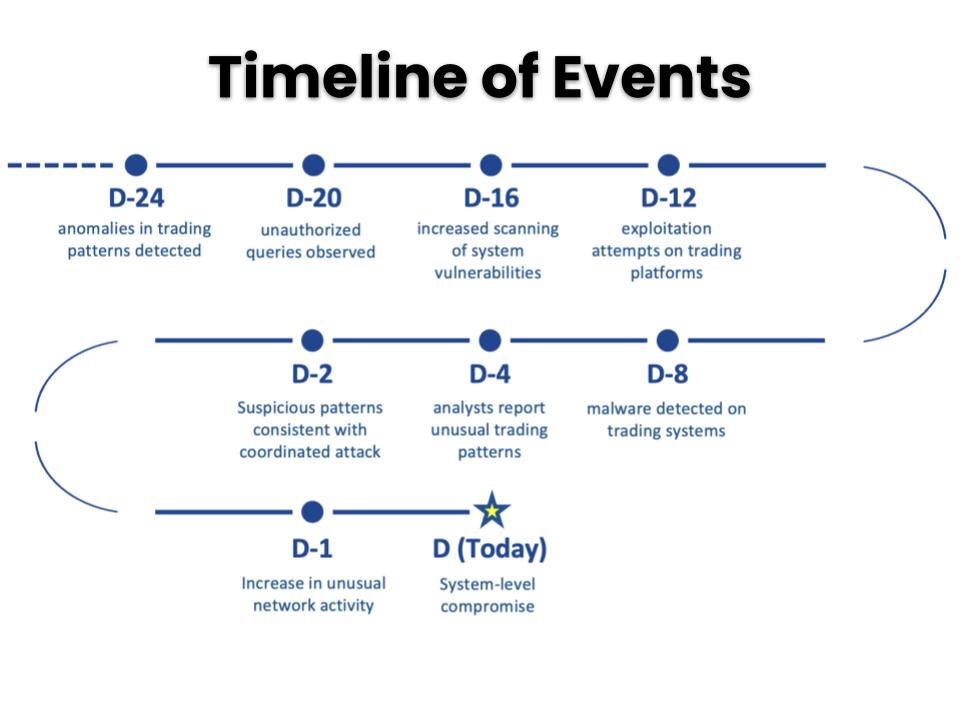



Updated Assessment
Four days have passed since the Mission Briefing identified the LSE as the target of a highly sophisticated Advanced Persistent Threat (APT).
- D: Mission Briefing
- D+1: subtle alterations in trading algorithms detected to manipulate market prices
- D+3: unauthorized access to latency-sensitive data identified (exploit arbitrage)
- D+4 (Today): encrypted data transmissions detected; suspected command and control (C2) communications to manage ongoing system manipulation activities, rather than large-scale data exfiltration
The assessment has reinforced the theory that the Syndicate is pursuing a dual-threat strategy for financial gain:
- Market Manipulation: The Syndicate's access to and modification of trading algorithms aim to artificially influence stock prices for fraudulent financial gain, likely to conduct a “pump and dump” scheme.
- Exploiting Latency Arbitrage: The unauthorized access to latency-sensitive data would allow the Syndicate to exploit small price differences across trading platforms, leveraging advanced knowledge of system vulnerabilities.
Given the sophistication of the threat and rapid progression of the tactics employed, there is an urgent need to decide on a response strategy. Your team has developed a list of response options, in collaboration with the NCSC, for your consideration. The urgency to select and implement the most appropriate response cannot be overstated. Your decision will not only directly impact the integrity and continuity of the LSE’s operations, but influence the broader trust and confidence in the global financial markets.
Task
Select the best strategy to neutralize the APT considering the key factors of maintaining continuity of operations, minimizing exposure, upholding public trust, and complying with legal and regulatory requirements.
Options
Explore the strategic response options available to the LSE in confronting the Silent Trader threat. Select a tab to read each option’s approach, advantages, and disadvantages.
- Option 1
- Option 2
- Option 3
- Option 4
- Option 5
- Option 6
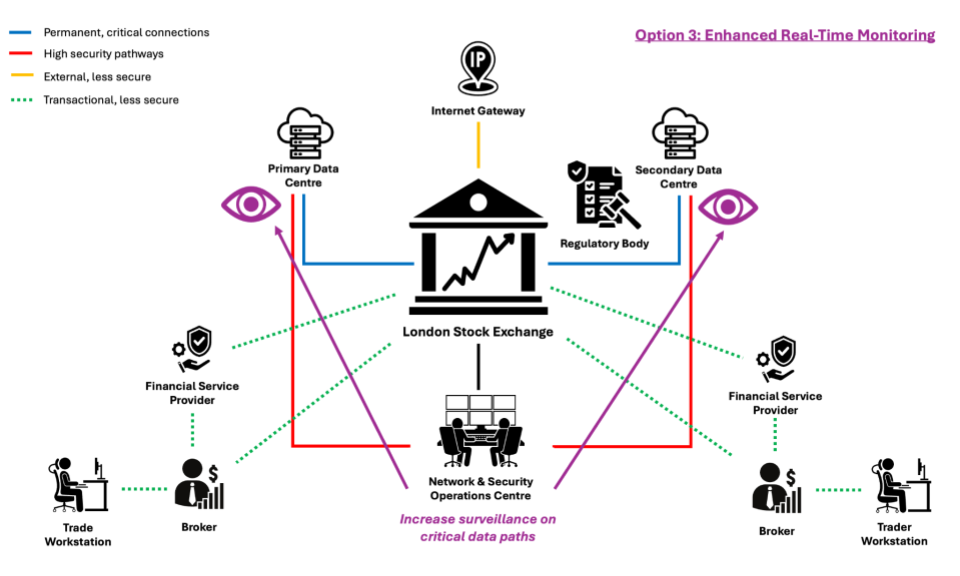
Option 1: Immediate System Lockdown
This option involves shutting down critical parts of the trading system to prevent further unauthorized access. The lockdown would be targeted at systems identified as compromised or at high risk. The implementation time is 1 hour and the technical risk is low to moderate.
Advantages
- prevents any further unauthorized transactions or data exfiltration assuming the APT have not already engineered an egress path out of your control
- limits the spread of the attack within the network
Disadvantages
- may cause significant disruption to trading activities, potentially affecting market stability
- risks financial losses due to halted trading operations
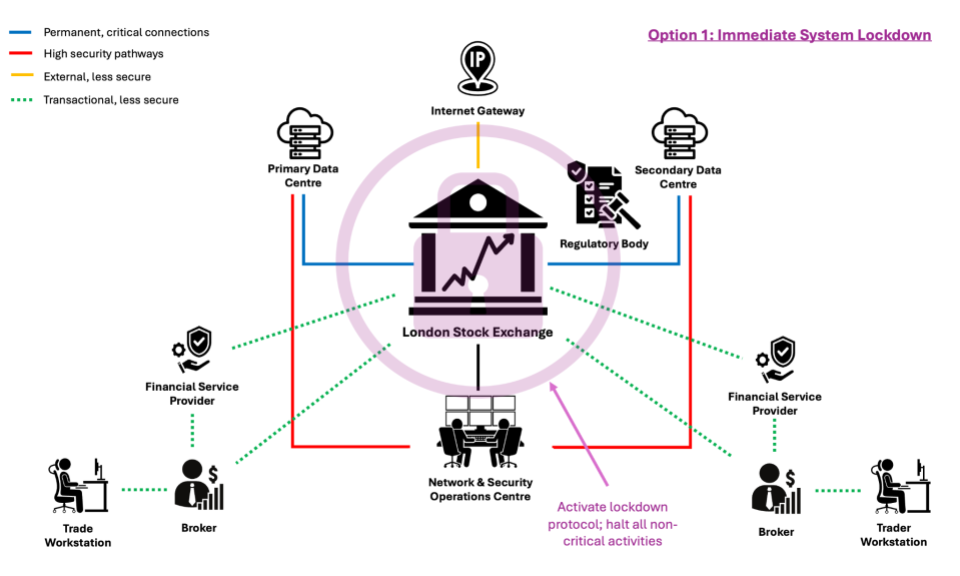
Option 2: Selective Network Segmentation
This strategy involves isolating sections of the network that are believed to be compromised, allowing parts of the system to continue operating while affected areas are dealt with. The implementation time is 2-3 hours and the technical risk is moderate, due to the need for precise network mapping and execution.
Advantages
- minimizes disruption to the overall trading system while addressing security breaches
- enhances the ability to monitor and contain the threat within segmented areas
Disadvantages
- complex to implement quickly; requires detailed knowledge of network architecture
- may not completely isolate the threat if lateral movement of the APT is not fully understood
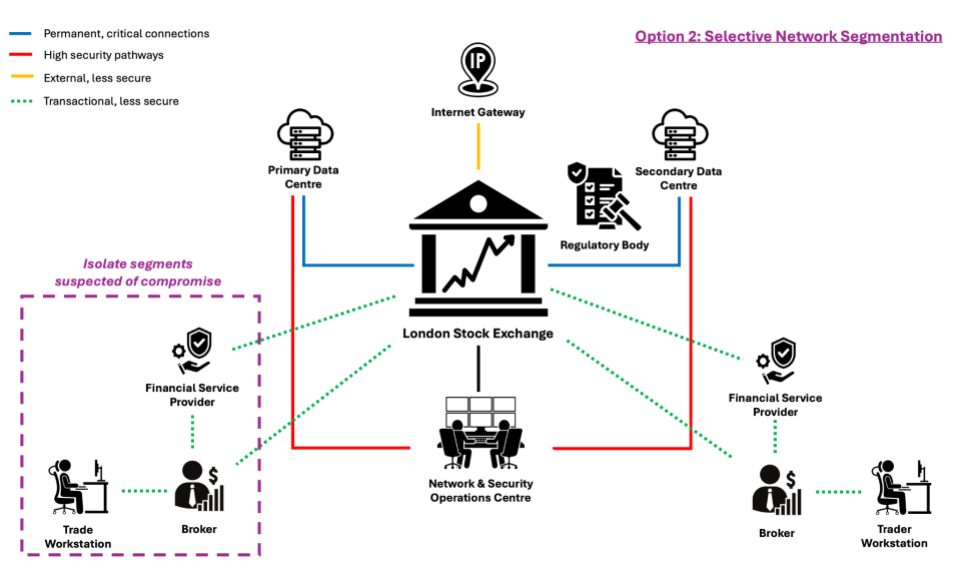
Option 3: Enhanced Real-Time Monitoring
Your approach is to upgrade system monitoring tools and protocols to detect unusual activities more efficiently and effectively, focusing on the most critical areas of the network and trading systems. The implementation time is 2 days and the technical risk is moderate to high to achieve the desired level of efficacy and using a streamlined deployment and systems integration approach.
Advantages
- increases the likelihood of detecting new threats or unusual patterns as they occur
- provides continuous data that can aid in swift response and future threat prevention
Disadvantages
- resource-intensive, requiring significant computational power and specialized personnel
- may generate false positives leading to unnecessary alarms and resource usage
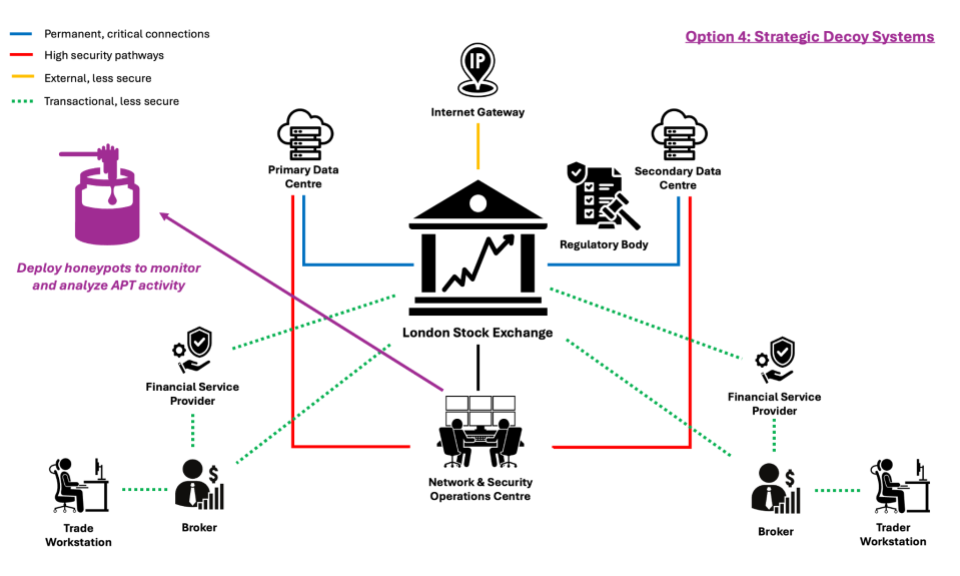
Option 4: Strategic Decoy Systems
This strategy involves setting up decoy servers or databases (i.e. honeypots) to mislead attackers into targeting non-critical system parts, thereby protecting valuable data and gathering intelligence on their methods. The implementation time is 2-3 days and the technical risk is high, due to the complexity of creating convincing decoys that are effective against sophisticated threats.
Advantages
- provides actionable intelligence on adversary methods, enhancing security measures
- can distract attackers from genuine targets, reducing risk to critical assets
Disadvantages
- requires resources to set up and maintain, potentially diverting attention from other critical security efforts
- only a temporary solution; does not eliminate the threat
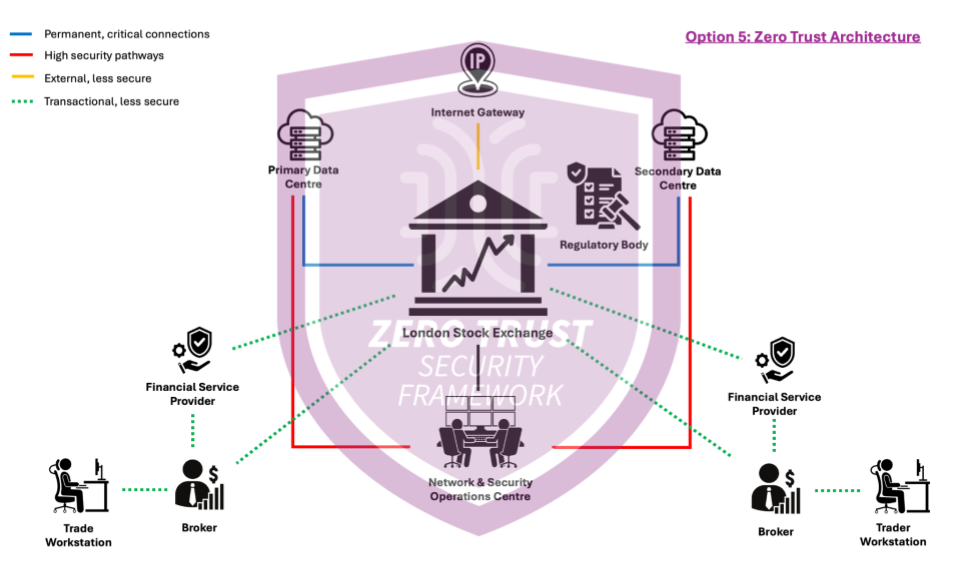
Option 5: Zero Trust Architecture
This option involves transitioning the LSE's cybersecurity framework to a Zero Trust model, where no entity inside or outside the network is trusted by default. All access requests are verified rigorously before granting access, ensuring that security is maintained through continuous validation of both credentials and device health. The implementation will take place incrementally over 3-6 months and the technical risk is assessed moderate to high due to the comprehensive changes required in both infrastructure and operational procedures.
Advantages
- Zero Trust minimizes unauthorized access by requiring continuous verification for all access attempts.
- Effectively adapts to evolving cyber threats and integrates new security technologies effectively.
Disadvantages
- An implementation requiring extensive changes to network and security policies, making it complex and time-consuming.
- Transitioning to Zero Trust can disrupt employee workflows and system access during implementation.
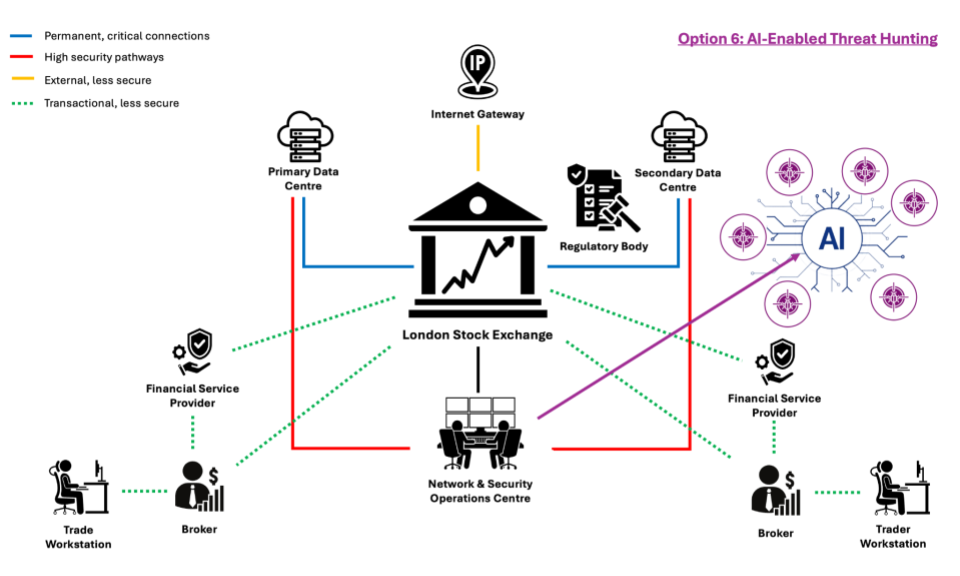
Option 6: AI-Enabled Threat Hunting
This approach leverages a combination of advanced threat hunting by cybersecurity experts and AI-driven automated defence systems to detect, respond, and neutralize threats in real time. Threat hunters use AI-enhanced tools to conduct deep investigations into potential malicious activity while automated defense mechanisms respond to and contain threats as they are identified.
Advantages:
- proactive detection by actively hunting for threats, identifying and neutralizing malicious actors before significant damage is done.
- automated response with AI systems can contain and respond to threats instantly, minimizing delay and human error
Disadvantages:
- complex integration requires sophisticated integration between AI tools and human operations, which can be resource-intensive
- potential for false positives with automated systems, necessitating manual oversight and intervention.
Decision
After reviewing the options, your team must now choose the response strategy that best aligns with Silent Trader’s mission objectives. Select one option below with 2 minutes (or less) remaining.
Option 1: Immediate System Lockdown
Option 2: Selective Network Segmentation
Option 3: Enhanced Real-Time Monitoring
Option 4: Strategic Decoy Systems
Option 5: Zero Trust Architecture
Option 6: AI-Enabled Threat Hunting